Diabetic Foot Ulcer
2 products
Showing 1 - 2 of 2 products
Complete Guide to Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment & Prevention
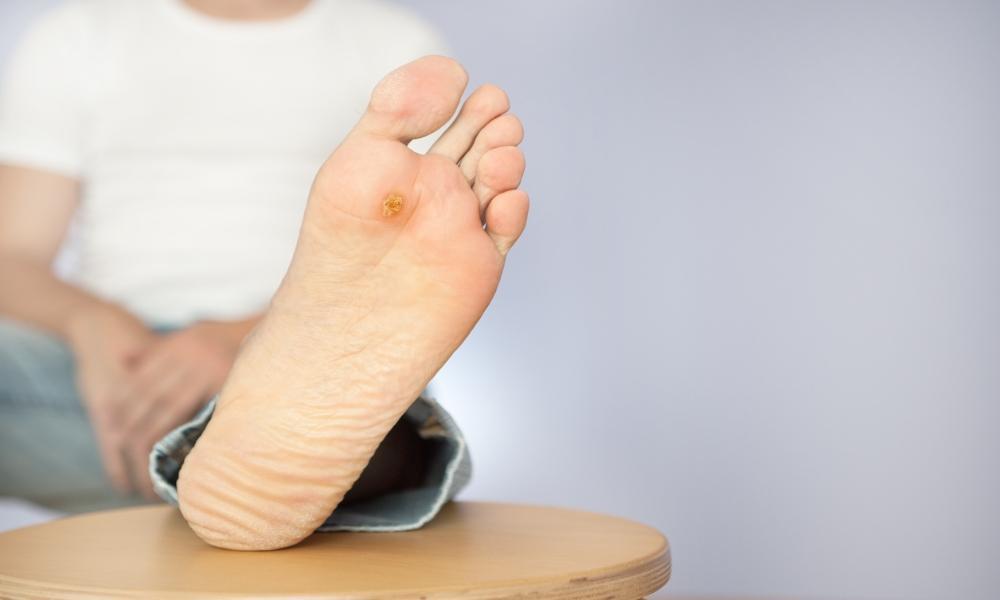
Diabetic foot ulcers affect approximately 15% of people with diabetes and are a leading cause of lower limb amputations. Early intervention with proper offloading footwear and medical treatment can prevent complications and promote healing. Our specialized diabetic foot ulcer products provide the pressure relief and protection needed for effective wound care.
Understanding Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetic foot ulcers are open sores or wounds that commonly occur on the bottom of the foot in people with diabetes. These ulcers develop due to a combination of factors including:
- Diabetic neuropathy - Nerve damage causing loss of sensation in feet
- Peripheral vascular disease - Poor blood circulation to extremities
- Pressure points - Repetitive stress on feet from walking
- Foot deformities - Charcot foot, bunions, or hammertoes
- Skin changes - Dry skin, calluses, and skin ulcers on feet
Common Symptoms & Warning Signs
Recognizing early signs of diabetic foot problems is crucial for preventing serious complications:
- Skin ulcers on feet or peeling skin on feet
- Diabetic foot pain or burning sensations
- Cold feet diabetes or feet cold diabetes symptoms
- Blood blister on toe diabetic or other skin changes
- Diabetic toe nails discoloration or thickening
- Problems with feet diabetes including numbness
- Antibiotic for foot ulcer needs or signs of infection
Treatment Solutions: Offloading Footwear
Proper offloading is the cornerstone of diabetic foot ulcer treatment. Our specialized products reduce pressure on wounds while allowing mobility:
For Plantar Wounds & Mild to Moderate Ulcers:
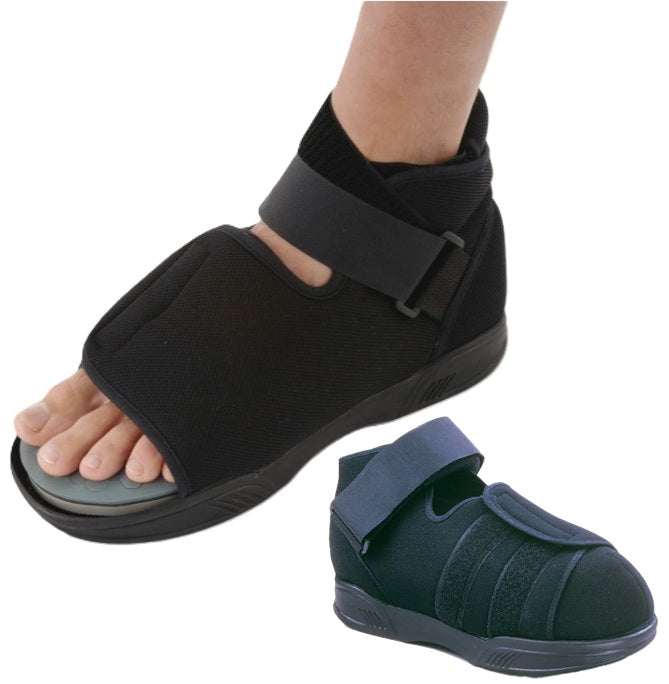
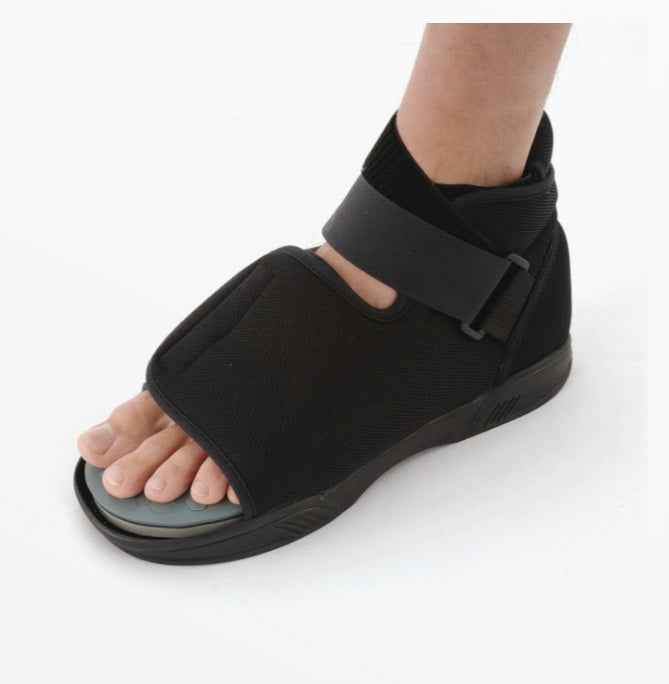
Ossur DH Diabetic Offloading Post Op Shoe - Ideal for short-term treatment (1-4 months) of plantar wounds. Features include:
- Patented active offloading insole that redistributes pressure away from ulcer sites
- Accommodates bulky dressings and total contact casts
- Removable toe piece for easy wound inspection without removing shoe
- Universal sizing fits either left or right foot
- Super-soft nylon upper prevents skin irritation
- Reinforced heel counter for stability
For Severe Plantar Ulcers & Extended Treatment:
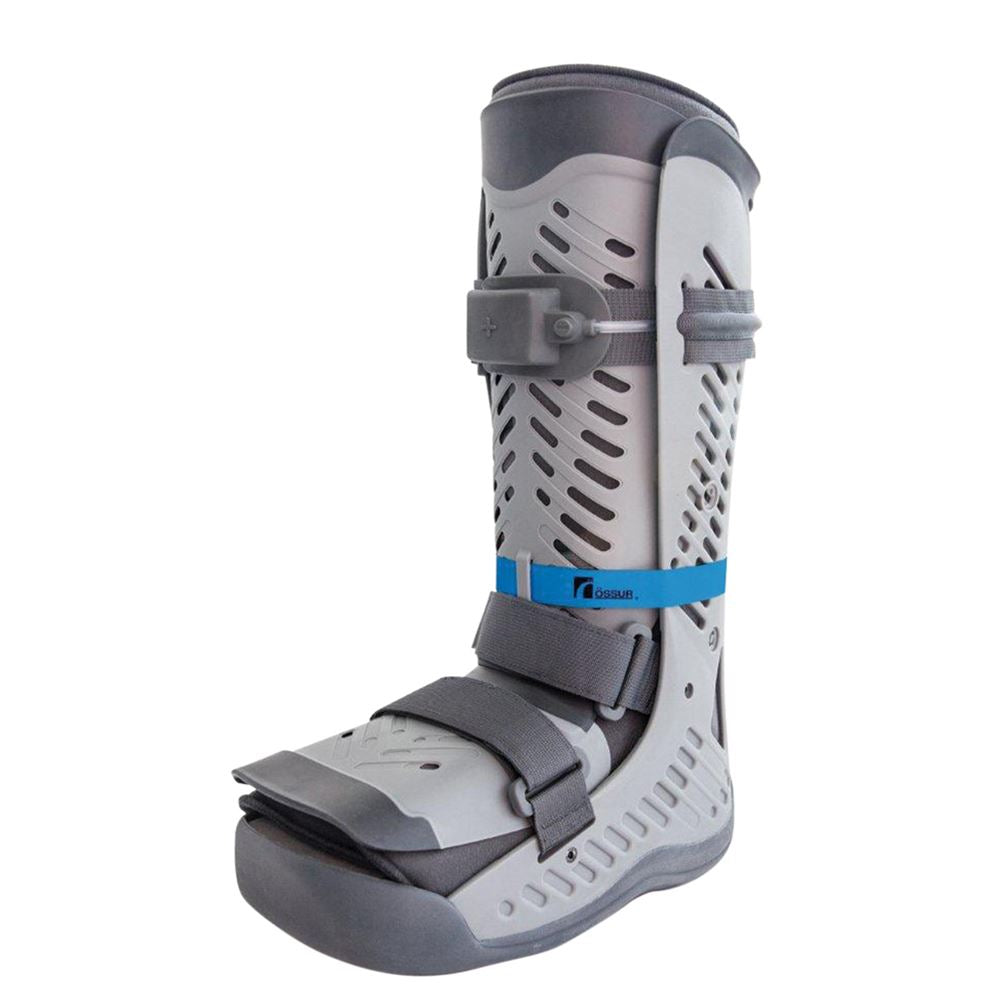
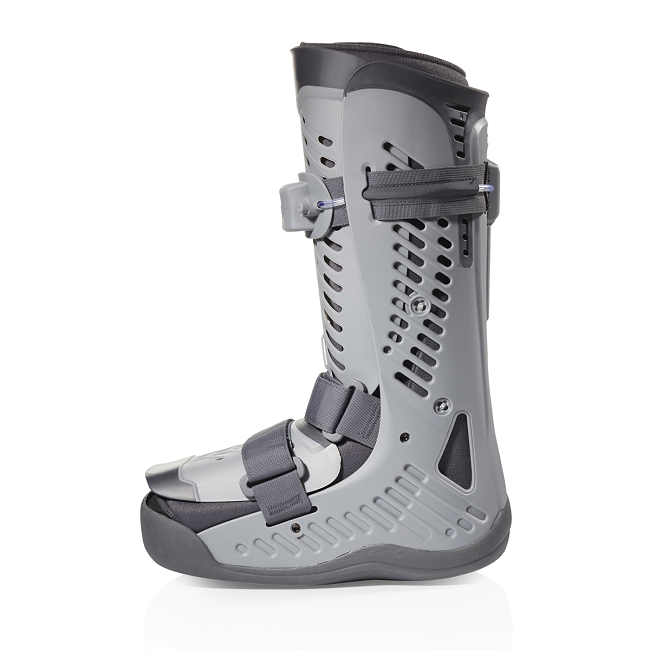
Ossur Rebound Diabetic Walking Boot - Advanced offloading for serious diabetic foot ulcers requiring maximum pressure relief:
- Tri-laminate insole with removable shock-absorbing hexagons for customized offloading
- Pressure relief valve allows precise pressure monitoring
- 90-degree foot/ankle immobilization prevents movement that could disrupt healing
- Flex Edge technology and rocker bottom outsole promote natural gait
- Machine washable liner for hygiene
- Tamper evident strapping ensures compliance
- Reimbursement code: L4361
Comprehensive Treatment Approach
Effective diabetic foot ulcer management requires multiple interventions:
Medical Treatment:
- Wound care - Regular debridement and dressing changes
- Infection control - Antibiotic for foot infection when needed
- Blood sugar management - Controlling type 2 diabetes feet complications
- Vascular assessment - Addressing circulation issues
Offloading & Protection:
- Specialized footwear - Diabetic foot pain relief through pressure redistribution
- Total contact casts - For severe cases requiring complete immobilization
- Custom orthotics - Long-term pressure management
Prevention Strategies:
- Daily foot inspections for skin ulcers on feet or changes
- Proper diabetic nails care and moisturizing for dry feet diabetes
- Wearing appropriate footwear at all times
- Regular podiatric examinations
- Managing underlying diabetes and circulation
When to Seek Immediate Care
Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience:
- New or worsening ulcers on feet
- Signs of infection (redness, warmth, drainage, odor)
- Severe diabetic foot pain
- Fever or chills
- Black or gangrenous tissue
- Charcot foot and diabetes symptoms (sudden swelling, redness, warmth)
Why Choose Our Diabetic Foot Ulcer Products?
- Authorized dealer - Genuine Ossur products with manufacturer warranty
- Clinically proven - Evidence-based offloading technology
- Insurance compatible - Reimbursement codes available
- Expert support - Guidance on product selection and fitting
- Fast shipping - Quick delivery when you need it most
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for a diabetic foot ulcer to heal?
Healing time varies based on ulcer severity, location, and overall health. With proper offloading and treatment, minor ulcers may heal in 1-2 months, while severe ulcers can take 4-6 months or longer. Consistent use of offloading footwear is critical for successful healing.
Can I walk with a diabetic foot ulcer?
Limited walking with proper offloading footwear is typically recommended. Our diabetic offloading shoes and boots allow necessary mobility while protecting the wound. Your healthcare provider will advise on activity restrictions based on your specific condition.
What is the difference between the DH Shoe and Rebound Boot?
The DH Shoe is ideal for mild to moderate plantar wounds requiring short-term offloading (1-4 months). The Rebound Boot provides maximum offloading for severe plantar ulcers, offers complete ankle immobilization, and includes advanced features like customizable pressure relief and monitoring capabilities.
Will insurance cover these products?
Many insurance plans cover diabetic offloading footwear when prescribed by a physician. The Ossur Rebound Boot has reimbursement code L4361. Contact your insurance provider to verify coverage and requirements.
Get the Right Solution for Your Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Don't let diabetic foot ulcers compromise your mobility and health. Our specialized offloading footwear provides the pressure relief needed for effective healing. Browse our collection to find the right solution for your needs, or contact our team for personalized product recommendations.